Modern Graphic Design: A Quick Overview
Modern Graphic design plays a vital role in shaping the digital world, especially for businesses seeking to engage their audience.
In our digital, image-driven culture, every industry and business uses graphic design to establish a strong brand identity.
So, how does graphic design impact business owners and why do we need it?
This article explores key elements of modern graphic design and its significant impact on successful marketing strategies.
What is Graphic Design, and Why is it Important?
Image: showing graphic design intersection arts, communication and psychology maybe? Or just show like different colors, shapes, lines, something to encompass what is graphic design
As we previously mentioned in our latest graphic design article, graphic design is made up of a variety of forms intersecting visual arts, communication, and psychology.
Graphic designers excel in conveying messages through visual elements such as images, typography, icons, shapes, colors, and lines.
Without graphic design, visual learners wouldn’t be able to understand the message that your business is trying to tell them.
That’s why it’s important to consider graphic design as a key method to success for your business, no matter what industry you are in.
Graphic designers can be seen as artists who channel their creative talents into purposeful art, focusing on communication rather than pure artistic expression. They transform complex ideas into accessible and engaging visual content, making information more digestible and aesthetically pleasing.
Modern graphic design touches nearly every aspect of our visual world, from traditional media like books and posters to digital platforms, including mobile apps and 3D animations.
Let’s explore the different ways where graphic designers apply their creative skills to solve problems and meet diverse needs.
Dispelling Myths: Is Graphic Design Just “Making Things Pretty”?
While making things “look pretty” is part of it, graphic design goes beyond just aesthetics. It’s about guiding the viewer’s eye and making sure the message comes through clearly.
Design connects with audiences and achieves goals by creating logos that communicate brand identity or infographics simplifying complex data.
They make sure that every visual element serves a purpose, making information more accessible, engaging, and memorable for everyone who interacts with it.
Which is why graphic design not only enhances aesthetics but also helps visual learners understand and connect with your brand’s story.
The role of graphic design in today’s digital world
We live in a very digital age. People process information holistically, linking messages with images, videos, and aesthetics.
We constantly decode visual messages while scrolling through our feeds, watching content, or passing signage.
New technologies like extended reality and smart interfaces transform graphic design, shaping experiences and perceptions wherever attention goes.
We can see the impact of well-executed design on businesses through:
- Creating visual appeal
- Enhancing user experience
- Building consistent brand identity
- Increasing brand awareness
- Conveying information efficiently
The Evolution of Graphic Designers
The evolution of graphic design stretches back hundreds of years ago. However, most design historians pinpoint the mid-20th century as the pivotal era when contemporary graphic design began to take form.
Several key developments characterize this transformation period:
1. Bauhaus and Swiss Style: Pioneers of Modern Graphic Design
International Typographic Style, also known as Swiss Style, was championed by visionary Swiss designers in the mid-20th century. Influenced by the Bauhaus movement, this style emphasizes minimalism and functionality, removing excess to focus on design essentials.
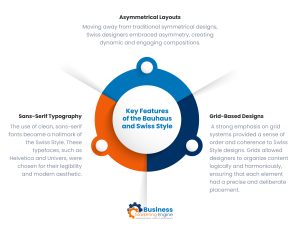
Key Features of the Bauhaus and Swiss Style
Image: could you help me with an idea of a graphic here? Maybe something showing bauhaus and swiss style graphics
- Asymmetrical Layouts: Moving away from traditional symmetrical designs, Swiss designers embraced asymmetry, creating dynamic and engaging compositions. This approach allowed for greater flexibility and creativity, enabling designers to break free from rigid structures and explore more innovative layouts.
- Sans-Serif Typography: The use of clean, sans-serif fonts became a hallmark of the Swiss Style. These typefaces, such as Helvetica and Univers, were chosen for their legibility and modern aesthetic. They complemented the minimalist approach, ensuring that the message was clear and direct without the distraction of ornate details.
- Grid-Based Designs: A strong emphasis on grid systems provided a sense of order and coherence to Swiss Style designs. Grids allowed designers to organize content logically and harmoniously, ensuring that each element had a precise and deliberate placement. This methodical approach to layout design helped in achieving a balanced and aesthetically pleasing composition.
Aesthetic Approach and Influence
The aesthetic approach of the Bauhaus and Swiss Style was grounded in clarity, objectivity, and concise visual communication.
By prioritizing functionality and simplicity, this style aimed to convey information in the most efficient and straightforward manner possible.
The influence of this design philosophy extended beyond graphic design, impacting architecture, industrial design, and even modern web design.
2. Digital Transformation: Revolutionizing the Design Process
The latter half of the 20th century witnessed a profound transformation in the graphic design industry, driven by rapid advancements in technology.
Innovations such as photo editing software, offset printing, and early computers revolutionized the way designers worked, marking the beginning of a new era in design.
Technological Innovations and Their Impact
- Photo Editing Software: The introduction of photo editing tools like Adobe Photoshop in the late 1980s revolutionized the graphic design process. Designers could now manipulate images with unprecedented ease, experimenting with colors, textures, and effects to achieve their desired look. This opened up new possibilities for creativity and innovation, allowing for more complex and visually striking designs.
- Offset Printing: Offset printing technology significantly improved the quality and efficiency of print production. This method allowed for sharper images, vibrant colors, and quicker turnaround times, making high-quality prints more accessible. Designers could now produce professional-grade materials with greater consistency and accuracy.
- Early Computers and Digital Tools: The advent of computers and digital design tools like Adobe Illustrator and CorelDRAW provided designers with powerful new capabilities. These tools enabled precise vector illustrations, intricate typographic designs, and detailed layouts. The ability to save and edit work digitally also streamlined the design process, making it faster and more efficient.
Scope for Experimentation
With these technological advancements, designers were no longer constrained by the limitations of traditional methods.
The digital revolution brought about a new era of experimentation and innovation, allowing for greater exploration of styles and techniques.
Designers could push the boundaries of creativity, blending different mediums and experimenting with new forms of visual communication.
3. Modern Graphic Design: Embracing Postmodernism and Beyond
As the 20th century drew to a close, graphic design underwent another significant transformation, influenced by the broader cultural and artistic shifts of the time. Postmodern art movements began challenging established norms and conventions, questioning what constituted originality and authenticity in art and design.
The Impact of Postmodernism
- Challenging Old Rules: Postmodernism rejected the rigid rules and structures of modernism, embracing a more eclectic and inclusive approach to design. This movement encouraged designers to break free from traditional constraints, exploring unconventional and diverse styles.
- Parody and Pastiche: One of the defining characteristics of postmodern graphic design was the use of parody and pastiche. Designers began referencing and reinterpreting historical styles, blending different influences to create new and unique visual expressions. This approach celebrated the idea of borrowing and remixing, challenging the notion of originality.
- Breaking Traditional Rules: Postmodern designers often defied conventional design principles, playing with asymmetry, distortion, and fragmentation. This experimental approach led to the creation of bold and dynamic designs that captured the essence of contemporary culture and society.
A New Era of Creativity and Innovation
The postmodern shift set the stage for graphic design to enter a period of rapid growth and diversification as the industry moved into the 21st century.
With digital tools becoming increasingly sophisticated and accessible, designers had unprecedented freedom to explore new ideas and techniques.
The 21st Century and Beyond
In the 21st century, graphic design has continued to evolve, embracing new technologies and trends.
The rise of the internet and social media has created new platforms for visual communication.
Artificial intelligence and virtual reality are opening up exciting new possibilities for interactive and immersive design experiences.
Today’s designers operate in a diverse and dynamic landscape, where the lines between different design disciplines are increasingly blurred.
This interdisciplinary approach fosters innovation and creativity, allowing designers to create impactful and engaging visual experiences that resonate with audiences worldwide.
In conclusion, the evolution of graphic design from the Bauhaus and Swiss Style to the digital transformation and postmodernism has been marked by continuous innovation and creativity. Each phase has built upon the previous one, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in design.
As we move further into the 21st century, the future of graphic design promises to be even more exciting, with new technologies and ideas shaping the way we communicate visually.
The Foundational Elements of Modern Graphic Design
Image: show a visual hierarchy and the key principles
Graphic design combines art and technology to communicate ideas visually. Effective graphic design captivates, informs, and leaves a lasting impression.
Let’s explore the key elements that every designer should know to create great visual experiences.
Visual Hierarchy & Composition
Visual hierarchy is all about organizing elements to guide how people look at information. By using techniques like size, color, and where things are placed, designers lead viewers to notice what’s most important first.
Whether it’s creating balance with symmetrical or asymmetrical designs, good composition helps make designs attractive and easy to understand.
It ensures that important details stand out while keeping everything visually pleasing and easy to follow.
Guiding the Viewer’s Eye
Good design leads the viewer’s eye to the most important information first through strategic placement, size, color, and contrast.
Key Principles
- Balance: Achieving equilibrium in design, whether symmetrical or asymmetrical.
- Contrast: Using differences in color, size, shape, or texture to highlight important elements.
- Repetition: Repeating elements to create consistency and rhythm.
- Proximity: Grouping related items together to organize information.
Color Theory
Color influences mood, perception, and brand recognition. Understanding color theory helps designers use color to feel different emotions —like blue for a sense of calmness, or red for passion.
Designers choose colors to match a brand’s personality, set the right mood, and ensure the message is clear and attention-grabbing.
Color theory helps create designs that not only look good but also connect with people emotionally.
Color Psychology and Brand Association
Colors affect emotions and brand perception. For example, blue conveys trust, while red evokes excitement. Choose colors that match the brand’s personality and desired emotional response.
For more on color theory, see our dedicated post on Color Theory.
Typography
What is typography?
Typography is everywhere we look. It’s in the blogs we read, on the websites we visit, even in everyday life – on product packaging, bumper stickers, and TV shows.
But what exactly is typography?
Simply put, typography is the style or arrangement of text. It can also refer to the art of arranging letters to make text legible, clear, and visually appealing.
Serif fonts
Image: show an example of serif fonts
Serif got its name because Serif fonts have little strokes called serifs attached to the main part of the letter.
They made a good choice for more traditional projects since they have a classical look and feel to them. They’re also traditional choices for body text in printed books and novels.
Sans serif fonts
Image: show an example of sans serif fonts
Sans serif fonts don’t have the extra strokes (serifs) found in serif fonts. This is because the name Sans is French for “without serif.”
Without the strokes, this style is considered to be more clean and modern. They are also easier to read on digital screens like smartphones and tablets.
Display fonts
Image: show an example of display fonts
Display fonts come in a wide variety of styles, each offering unique characteristics and aesthetic apples. From graceful script fonts that are elegant and sophisticated to bold blackletter fonts that exude a sense of tradition and history.
Then there are all-caps fonts, which command attention and convey strength with their bold, uppercase letters. You also can’t forget display fonts that are simply fancy and capture attention with their intricate details and artistic flair.
However, because of their decorative nature, it’s better to use display fonts for small amounts of text, like titles and headers and more graphic-heavy designs.
Choosing Fonts
In a sense, fonts have their own language. A modern font might suggest innovation, while a handwritten font suggests creativity. They can come across as casual, neutral, exotic, or even graphic.
That’s why it’s important to understand the message you’re trying to get across first, and then choose a font that fits.
Fonts to avoid
Some fonts come with unnecessary extra baggage, including Comic Sans, Curlz, and Papyrus. While there isn’t anything particularly wrong with these fonts – it’s best to stay away from them since they have a reputation for being outdated and overused.
They can be tempting to incorporate into your graphic design, but make sure to think twice when considering them.
There are plenty of other fonts with similar look and feel that are less likely to detract from your overall message.
Readability and Hierarchy
Readable type is crucial. A clear typographic hierarchy, with different font sizes and styles, helps guide the viewer through the content.
For more on typography, see our dedicated post on Typography.
Imagery & Illustration
Images and illustrations enhance visual storytelling, creating emotional connections and making designs more engaging.
Selecting Photos and Creating Illustrations
High-quality, relevant photos or custom illustrations can differentiate a brand and make its message memorable. Choose visuals that are aesthetically pleasing and aligned with the brand’s message.
Style and Relevance
Consistent visual style reinforces brand identity. Whether using photos, minimalist graphics, or vibrant illustrations, the style should match the brand’s voice.
For more on imagery, see our dedicated post on Imagery & Illustration.
Design Software
The right tools can enhance creativity and workflow. Here are some popular design software options:
- Adobe Photoshop: For photo editing and detailed digital artwork.
- Adobe Illustrator: For vector graphics, logo design, and illustrations.
- Sketch: For web and mobile interface design.
- Figma: For collaborative design work, especially in UI/UX design.
Modern Trends in Graphic Design
Image: anything showing off modern trends in graphic design so modern graphics or so
Graphic design is a dynamic field that continually evolves, influenced by technological advancements, cultural shifts, and changing consumer preferences. New trends emerge regularly, shaping how designers approach visual communication and pushing the boundaries of creativity and functionality. Let’s delve into some of the prominent trends that are currently influencing modern graphic design practices.
Minimalism
Minimalism in design is a trend that focuses on simplicity and clarity, stripping away unnecessary elements to highlight what is essential.
This approach aligns with the philosophy of “less is more.”
- Key Characteristics:
- Clean Typography: Minimalist designs often use sans-serif fonts that are easy to read and contribute to a clean, modern look.
- Ample White Space: White space, or negative space, is strategically used to create a sense of openness and improve readability.
- Restrained Color Palette: A limited color palette is employed to avoid overwhelming the viewer and to maintain a cohesive visual identity.
- Benefits:
- Enhanced Visual Appeal: The simplicity of minimalist design creates a sleek and elegant look that is aesthetically pleasing.
- Improved Usability: By reducing clutter, minimalist designs make it easier for users to navigate and focus on the content, enhancing overall user experience.
- Timeless Quality: Minimalist designs often have a timeless quality, avoiding the rapid obsolescence associated with more complex and trend-driven designs.
Microinteractions & User Experience (UX) Focus
Microinteractions are subtle design elements that provide feedback or guidance in response to user actions. These small details play a crucial role in enhancing the overall user experience, making interfaces more intuitive and enjoyable to use.
- Examples of Microinteractions:
- Button Animations: Visual feedback when a button is clicked, indicating that the action has been registered.
- Hover Effects: Changes in an element’s appearance when the user hovers over it with their cursor, providing a sense of interactivity.
- Loading Animations: Animated indicators that inform users that a process is underway, reducing perceived waiting time.
- Importance of UX:
- Intuitive Interfaces: Modern graphic design places a strong emphasis on creating interfaces that are easy to navigate, ensuring that users can achieve their goals with minimal effort.
- Seamless Interactions: Designers aim to create seamless interactions that feel natural and intuitive, enhancing the overall user experience.
- User Delight: Thoughtfully designed micro-interactions can delight users, making the experience memorable and engaging.
Data Visualization & Storytelling
Data visualization involves presenting complex information in a visually engaging way that tells a compelling story. This trend is increasingly important as the amount of data we generate and consume continues to grow.
- Types of Data Visualization:
- Charts and Graphs: Traditional tools like bar charts, line graphs, and pie charts are used to represent quantitative data clearly.
- Infographics: These combine text, images, and data to create informative and visually appealing narratives.
- Interactive Visualizations: Tools that allow users to interact with the data, exploring different aspects and uncovering insights dynamically.
- Benefits of Data Visualization:
- Accessibility: Visual representations of data make complex information more accessible and easier to understand for a broader audience.
- Engagement: Well-designed visualizations can capture the audience’s attention and keep them engaged with the content.
- Informed Decision-Making: Effective data storytelling helps audiences grasp key insights quickly, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Additional Modern Trends in Graphic Design
Bold Typography
Bold typography is a trend where designers use large, eye-catching fonts to create a strong visual impact. This approach can convey messages powerfully and attract attention in a crowded visual landscape.
- Characteristics:
- Oversized Text: Large font sizes are used to make headlines and key messages stand out.
- Creative Typefaces: Unique and custom typefaces add personality and uniqueness to the design.
- Contrasting Colors: High contrast between text and background ensures readability and draws the viewer’s eye.
Sustainable Design
Sustainable design is gaining prominence as awareness of environmental issues grows. This trend involves creating designs that are environmentally friendly and promote sustainability.
- Principles:
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Using recycled or sustainable materials in print design.
- Digital Alternatives: Focusing on digital media to reduce paper waste.
- Minimalist Approach: Reducing resource use by simplifying designs and production processes.
3D Design and Typography
3D design and typography are becoming increasingly popular, offering depth and realism that traditional flat designs cannot achieve. This trend leverages advanced software and technologies to create stunning visual effects.
- Applications:
- Product Visualizations: Realistic 3D models for product presentations and marketing.
- Interactive Experiences: Engaging 3D elements in websites and applications.
- Typographic Experiments: Using 3D techniques to create unique and dynamic text treatments.
Mixed Media and Collage
Mixed media and collage combine various materials and techniques to create visually rich and textured designs. This approach can add depth and intrigue, making designs stand out.
- Elements:
- Photographs: Integrating real-world images with digital elements.
- Textures: Adding tactile elements to enhance the sensory experience.
- Hand-Drawn Elements: Incorporating sketches and illustrations for a personal touch.
Augmented Reality (AR) in Design
(Image: maybe a fun AR graphic/image here)
Augmented Reality (AR) is transforming how we interact with design, blending digital elements with the physical world. This technology offers immersive experiences and new ways to engage audiences.
- Uses in Graphic Design:
- Interactive Print Media: Scannable AR codes on print materials that lead to interactive digital experiences.
- Retail Experiences: Virtual try-ons and product demonstrations using AR.
- Brand Engagement: Creative AR campaigns that enhance brand storytelling and user engagement.
The Rise of User-Generated Content (UGC) & Its Design Implications
User-generated content, such as social media posts, reviews, and images created by users, has become a powerful force in marketing and branding.
Designers now integrate UGC into campaigns to build authenticity and community around brands. This trend emphasizes the need for designs that can adapt and incorporate user-generated visuals seamlessly.
Accessibility & Inclusive Design Practices
Accessibility ensures that designs are usable by people of all abilities, including those with disabilities.
Inclusive design considers diverse user needs and preferences from the outset of the design process.
Designers prioritize creating experiences that are accessible, accommodating, and respectful of all users.
Putting it All Together: The Graphic Design Process
Image: showing maybe like a step by step process for making graphics
Creating graphics involves a process that ensures designs meet objectives and resonates with the intended audience.
The goal is to achieve a balance between aesthetics and functionality.
This comprehensive approach encompasses various stages, each critical to the final product’s success.
Defining Project Goals and Target Audience
Establishing Clear Objectives
The foundation of any successful graphic design project lies in establishing clear and measurable objectives.
These goals serve as a roadmap, guiding the design process and ensuring that every decision aligns with the overarching purpose. Objectives might include increasing brand awareness, promoting a product or service, improving user engagement, or conveying specific information effectively.
Identifying the Target Audience
Equally important is identifying and understanding the target audience. This involves demographic research, including age, gender, location, and socioeconomic status.
It also includes psychographic analysis, which delves into the audience’s interests, values, and behaviors.
Understanding the audience’s needs and preferences ensures that the design resonates and engages effectively.
Research, Brainstorming, and Concept Development
Conducting Thorough Research
Before any design work begins, extensive research is essential. This research covers various areas:
- Audience Insights: Understanding what appeals to the target audience, including cultural nuances and psychological triggers.
- Industry Trends: Staying updated with current design trends and standards within the industry to ensure relevance and competitiveness.
- Competitive Analysis: Examining competitors’ designs to identify strengths and weaknesses, and to find opportunities for differentiation.
Brainstorming Sessions
Brainstorming is a collaborative process where designers, stakeholders, and sometimes even clients come together to generate a wide array of ideas. These sessions encourage free-thinking and creativity, allowing participants to propose concepts without the constraints of feasibility at this initial stage. Techniques such as mind mapping, free writing, and sketching can help in unleashing creative potential.
Concept Development
Once a pool of ideas has been generated, the next step is to refine these ideas into concrete concepts. This involves selecting the most promising ideas and developing them further through sketches, mood boards, and preliminary mock-ups. Concept development is about exploring different visual directions, testing how well they align with the project goals and audience expectations.
Design Iteration and Refinement
Initial Design Creation
With a clear concept in place, designers move on to creating initial designs. These are usually rough drafts that capture the essence of the concept but are open to significant changes. This phase involves experimenting with different layouts, color schemes, typography, and imagery to find the most effective combinations.
Iterative Feedback Loops
Design is an iterative process. Initial designs are reviewed and critiqued by stakeholders, team members, and sometimes the target audience. Constructive feedback is crucial at this stage, as it highlights areas for improvement and helps ensure the design meets its objectives. Designers make revisions based on this feedback, refining details and enhancing the overall quality of the design.
Importance of User Testing and Feedback
Conducting User Testing
User testing is a pivotal phase where real users interact with the design. This testing can take various forms, such as usability testing, A/B testing, or focus groups.
The aim is to gather first hand feedback on how users perceive and interact with the design, identifying any usability issues or areas of confusion.
Evaluating Usability and Accessibility
Usability and accessibility are key components of user testing. Usability testing assesses how easily users can navigate and understand the design, ensuring
It is intuitive and straightforward. Accessibility testing ensures that the design is usable by people with disabilities, adhering to standards such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
Iterative Testing and Refinement
User feedback is invaluable for making informed refinements to the design. This iterative process involves revising the design based on user input, then testing again to ensure the changes have effectively addressed any issues. This cycle continues until the design meets user expectations and delivers a seamless experience.
Finalization and Production
Preparing Final Designs
Once the design has been thoroughly tested and refined, the final step is to prepare the design for production. This involves creating high-resolution files, ensuring all elements are correctly aligned and formatted, and preparing specifications for printing or digital deployment.
Quality Assurance
Before the design goes live, a final quality assurance check is essential. This includes proofreading text, verifying colors and image quality, and ensuring that all interactive elements function correctly. Quality assurance helps catch any last-minute errors and ensures the final product is polished and professional.
Launch and Post-Launch Analysis
After the design is launched, it’s important to monitor its performance and gather post-launch feedback. Analyzing metrics such as user engagement, conversion rates, and customer feedback provides insights into how well the design is achieving its objectives. This data can inform future design projects, creating a continuous loop of improvement and innovation.
Conclusion
By embracing modern trends such as minimalism, microinteractions, data visualization, user-generated content, and inclusive design practices, graphic designers can create impactful and user-centered designs.
The graphic design process—from defining goals and researching to iterative refinement and user testing—ensures that designs not only meet objectives but also resonate with and engage the intended audience effectively.
Embracing these trends and practices empowers designers to innovate and create compelling visual experiences in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Our expertise in design and branding will enhance your visual impact, ensuring your message stands out.
From creating brand logos to developing engaging marketing materials, we have the skills to take your design to the next level.
If you’re ready to up your graphic design game, contact us!
Let’s work together to bring your vision to life.